# React16.13源码解析
# 资料分享
React 基础:https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html
react hooks 基础:https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/hooks-intro.html
react调度机制:http://www.7km.top/main/scheduler#scheduleupdateonfiber
requestIdleCallback和requestAnimationFrame详解: https://juejin.im/post/6844903848981577735
messageChannel是什么:https://www.jianshu.com/p/4f07ef18b5d7
# React.children.map
React.Children 提供了用于处理 this.props.children 不透明数据结构的实用方法。
React.Children.map(children, function[(thisArg)])
在 children 里的每个直接子节点上调用一个函数,并将 this 设置为 thisArg。如果 children 是一个数组,它将被遍历并为数组中的每个子节点调用该函数。如果子节点为 null 或是 undefined,则此方法将返回 null 或是 undefined,而不会返回数组。
注意
如果
children是一个Fragment对象,它将被视为单一子节点的情况处理,而不会被遍历。
其实类似数组的map方法,但是做了更加全面的容错,接下来我们看一下源码:
ReactChildren.js
//首先我们找到这个js文件,找到输出,可以定位到 mapChildren方法
export {
forEachChildren as forEach,
mapChildren as map,
countChildren as count,
onlyChild as only,
toArray,
};
// 为什么要使用React.Children.map, 而不是直接使用this.props.children.map
// 1. React.Children.map是一种安全的用法,会默认判断null,undefined,对象,字符串等情况,即使类型不是Array,也不会报错
// 2. React.Children.map会默认展平多维数组
// 3. 迭代器也可以支持输出
function mapChildren(children, func, context) {
if (children == null) {
return children;
}
const result = [];
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, result, null, func, context);
return result;
}
function mapSingleChildIntoContext(bookKeeping, child, childKey) {
const {result, keyPrefix, func, context} = bookKeeping;
// func 就是我们在 React.Children.map(this.props.children, c => c)中传入的第二个函数参数
let mappedChild = func.call(context, child, bookKeeping.count++);
if (Array.isArray(mappedChild)) {
// 数组递归展平
// React.Children.map(this.props.children, c => [c, [c, [c]]])
mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(mappedChild, result, childKey, c => c);
} else if (mappedChild != null) {
if (isValidElement(mappedChild)) {
// 创建一个新的ReactElement
mappedChild = cloneAndReplaceKey(
mappedChild,
// Keep both the (mapped) and old keys if they differ, just as
// traverseAllChildren used to do for objects as children
keyPrefix +
(mappedChild.key && (!child || child.key !== mappedChild.key)
? escapeUserProvidedKey(mappedChild.key) + '/'
: '') +
childKey,
);
}
result.push(mappedChild);
}
}
function mapIntoWithKeyPrefixInternal(children, array, prefix, func, context) {
let escapedPrefix = '';
if (prefix != null) {
escapedPrefix = escapeUserProvidedKey(prefix) + '/';
}
const traverseContext = getPooledTraverseContext(
array,
escapedPrefix,
func,
context,
);
// 将嵌套的数组展平
traverseAllChildren(children, mapSingleChildIntoContext, traverseContext);
//mapSingleChildIntoContext 回调函数
releaseTraverseContext(traverseContext);
}
const POOL_SIZE = 10;
const traverseContextPool = [];
// 维护一个对象最大为10的池子,从这个池子取到对象去赋值,用完了清空, 防止内存抖动
// 可以循环使用,创建太多的话,也会占据内存
function getPooledTraverseContext(
mapResult,
keyPrefix,
mapFunction,
mapContext,
) {
if (traverseContextPool.length) {
const traverseContext = traverseContextPool.pop();
traverseContext.result = mapResult;
traverseContext.keyPrefix = keyPrefix;
traverseContext.func = mapFunction;
traverseContext.context = mapContext;
traverseContext.count = 0;
return traverseContext;
} else {
return {
result: mapResult,
keyPrefix: keyPrefix,
func: mapFunction,
context: mapContext,
count: 0,
};
}
}
function traverseAllChildren(children, callback, traverseContext) {
if (children == null) {
return 0;
}
return traverseAllChildrenImpl(children, '', callback, traverseContext);
}
function traverseAllChildrenImpl(
children,
nameSoFar,
callback,
traverseContext,
) {
const type = typeof children;
if (type === 'undefined' || type === 'boolean') {
// All of the above are perceived as null.
children = null;
}
// invokeCallback=true,才触发callBack执行
let invokeCallback = false;
if (children === null) {
invokeCallback = true;
} else {
switch (type) {
case 'string':
case 'number':
invokeCallback = true;
break;
case 'object':
switch (children.$$typeof) {
//如果props.children是单个ReactElement/PortalElement的话 必会触发invokeCallback=true
case REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE:
case REACT_PORTAL_TYPE:
invokeCallback = true;
}
}
}
// 处理非数组的情况
if (invokeCallback) {
callback(
traverseContext,
children,
// If it's the only child, treat the name as if it was wrapped in an array
// so that it's consistent if the number of children grows.
nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR + getComponentKey(children, 0) : nameSoFar,
);
return 1;
}
let child;
let nextName;
let subtreeCount = 0; // Count of children found in the current subtree.
const nextNamePrefix =
nameSoFar === '' ? SEPARATOR : nameSoFar + SUBSEPARATOR;
if (Array.isArray(children)) {
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
child = children[i];
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, i);
// 是数组就递归执行
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl(
child,
nextName,
callback,
traverseContext,
);
}
} else {
// 迭代器处理
const iteratorFn = getIteratorFn(children);
if (typeof iteratorFn === 'function') {
if (disableMapsAsChildren) {
invariant(
iteratorFn !== children.entries,
'Maps are not valid as a React child (found: %s). Consider converting ' +
'children to an array of keyed ReactElements instead.',
children,
);
}
if (__DEV__) {
// Warn about using Maps as children
if (iteratorFn === children.entries) {
if (!didWarnAboutMaps) {
console.warn(
'Using Maps as children is deprecated and will be removed in ' +
'a future major release. Consider converting children to ' +
'an array of keyed ReactElements instead.',
);
}
didWarnAboutMaps = true;
}
}
const iterator = iteratorFn.call(children);
let step;
let ii = 0;
while (!(step = iterator.next()).done) {
child = step.value;
nextName = nextNamePrefix + getComponentKey(child, ii++);
// 遍历
subtreeCount += traverseAllChildrenImpl(
child,
nextName,
callback,
traverseContext,
);
}
} else if (type === 'object') {
let addendum = '';
if (__DEV__) {
addendum =
' If you meant to render a collection of children, use an array ' +
'instead.' +
ReactDebugCurrentFrame.getStackAddendum();
}
const childrenString = '' + children;
invariant(
false,
'Objects are not valid as a React child (found: %s).%s',
childrenString === '[object Object]'
? 'object with keys {' + Object.keys(children).join(', ') + '}'
: childrenString,
addendum,
);
}
}
return subtreeCount;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
# react fiber 的大致思路
为什么要用fiber调度, 它解决了什么问题?
react16以前的调度算法, 采用自顶向下递归,更新整个子树,这个过程不可打断,不可取消,如果子树特别大的话,主线程就会一直被占用,会造成页面的掉帧,出现卡顿。
react16推出的fiber调度, 分为两个阶段,一个是reconciliation阶段,2是commit阶段,在reconciliation阶段:fiber在执行过程中以fiber为基本单位,每执行完一个fiber,都会有一个询问是否有优先级更高的任务的一个判断,如果有优先级更高的任务进来,就中断当前执行,先执行优先级更高的任务。这个阶段会进行dom diff, 生成workInProgressTree,并标记好所有的side effect
2.1 数值结构变成了链表结构
2.1 任务+过期时间/优先级
2.2 reconciliation可以被打断,不会渲染到页面上的;commit阶段,一次执行完。side effect
- commit阶段,处理所有的 side effect , 执行更新操作。此阶段不可中断
# React
react的3种启动方式 (https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/concurrent-mode-adoption.html#why-so-many-modes)
Legacy模式
Concurrent模式
Blocking模式: 做为Legacy和Concurrent之间的过度
# ReactDom.render流程
# ReactDom.render 分析
创建 reactRoot,在dom元素上挂载, FiberRoot
Root: { _reactRootContainer: RootType } RootType: { _internalRoot: FiberRoot } FiberRoot: { // 当前应用对应的Fiber对象 current: uninitializedFiber, FiberNode // root节点 containerInfo: containerInfo, // 指向当前已经完成准备工作的Fiber Tree Root, 在commit阶段处理 finishedWork: null, // Fiber, 链表结构 // 过期时间 expirationTime: NoWork, } FiberNode : { // FiberNode的类型 this.tag = tag; this.key = key; this.elementType = null; // Function|String|Symbol|Number|Object this.type = null; this.stateNode = null; // 深度优先遍历的 // Fiber 表示父级 FiberNode this.return = null; // 表示第一个子 FiberNode this.child = null; // 表示紧紧相邻的下一个兄弟 FiberNode this.sibling = null; this.index = 0; // 拿到真实的dom实例 this.ref = null; // 表示新的props this.pendingProps = pendingProps; // 当前fiber的旧props this.memoizedProps = null; // 更新队列,队列内放着即将要发生的变更状态 this.updateQueue = null; // 最终会遍历这个update链表 // 表示经过所有流程处理后的当前的state this.memoizedState = null; this.contextDependencies = null; this.mode = mode; // effectTag 更新类型,例如, replace, delete, update this.effectTag = NoEffect; // 下一个将要处理的副作用F this.nextEffect = null; // 第一个需要处理的副作用 this.firstEffect = null; // 最后一个将要处理的副作用F this.lastEffect = null; // 过期时间是和优先级有关 this.expirationTime = NoWork; // 子fiber中优先级最高的filber this.childExpirationTime = NoWork; // 连接上一个状态的fiber,储存了之前的镜像 this.alternate = null; // 上一次更新时的旧Fiber = WorkInProgress.alternate }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64调用 unbatchUpdate 非批处理
调用 updateContainer
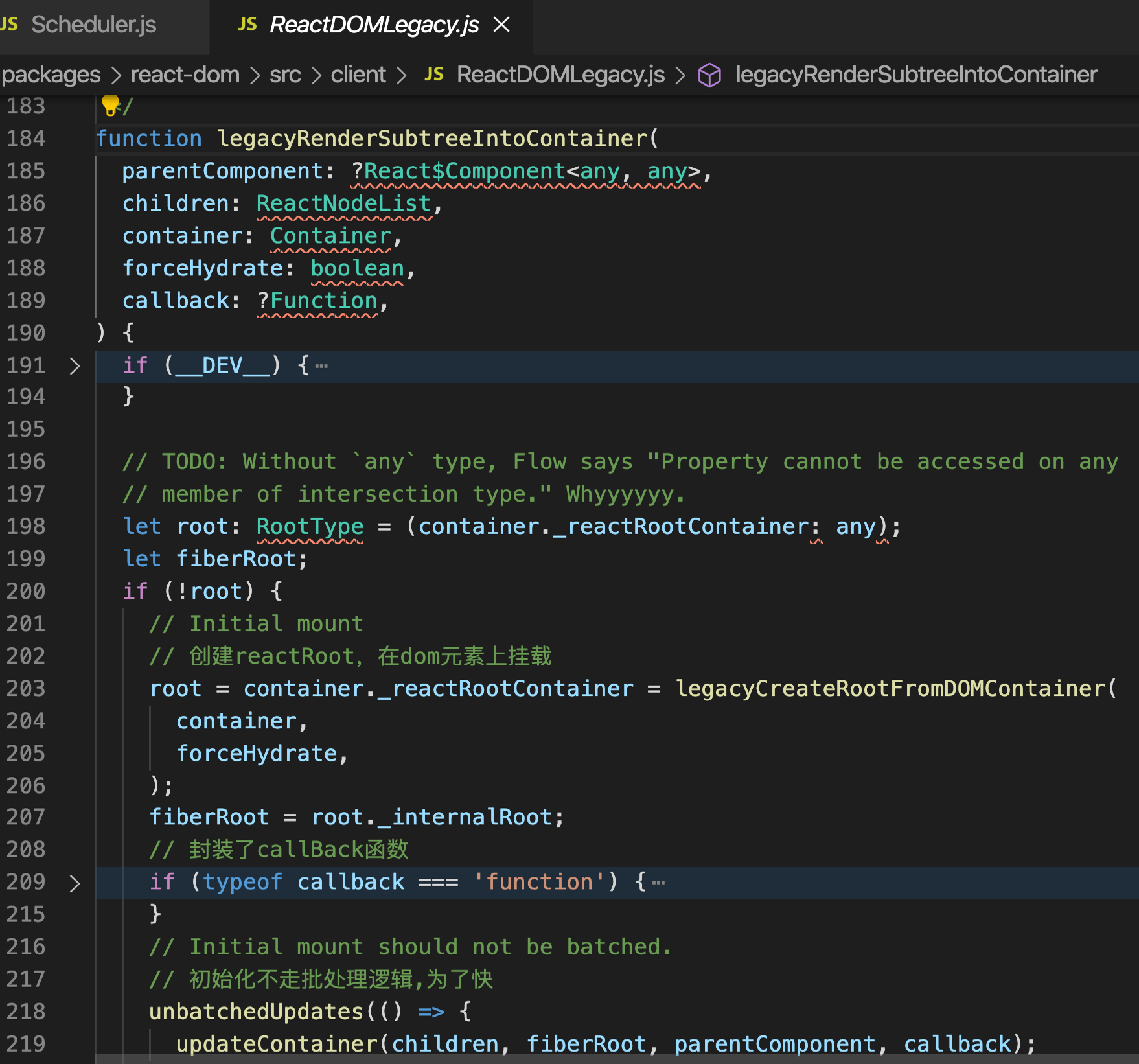
render函数返回了legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer函数处理后的结果
拿到FiberNode
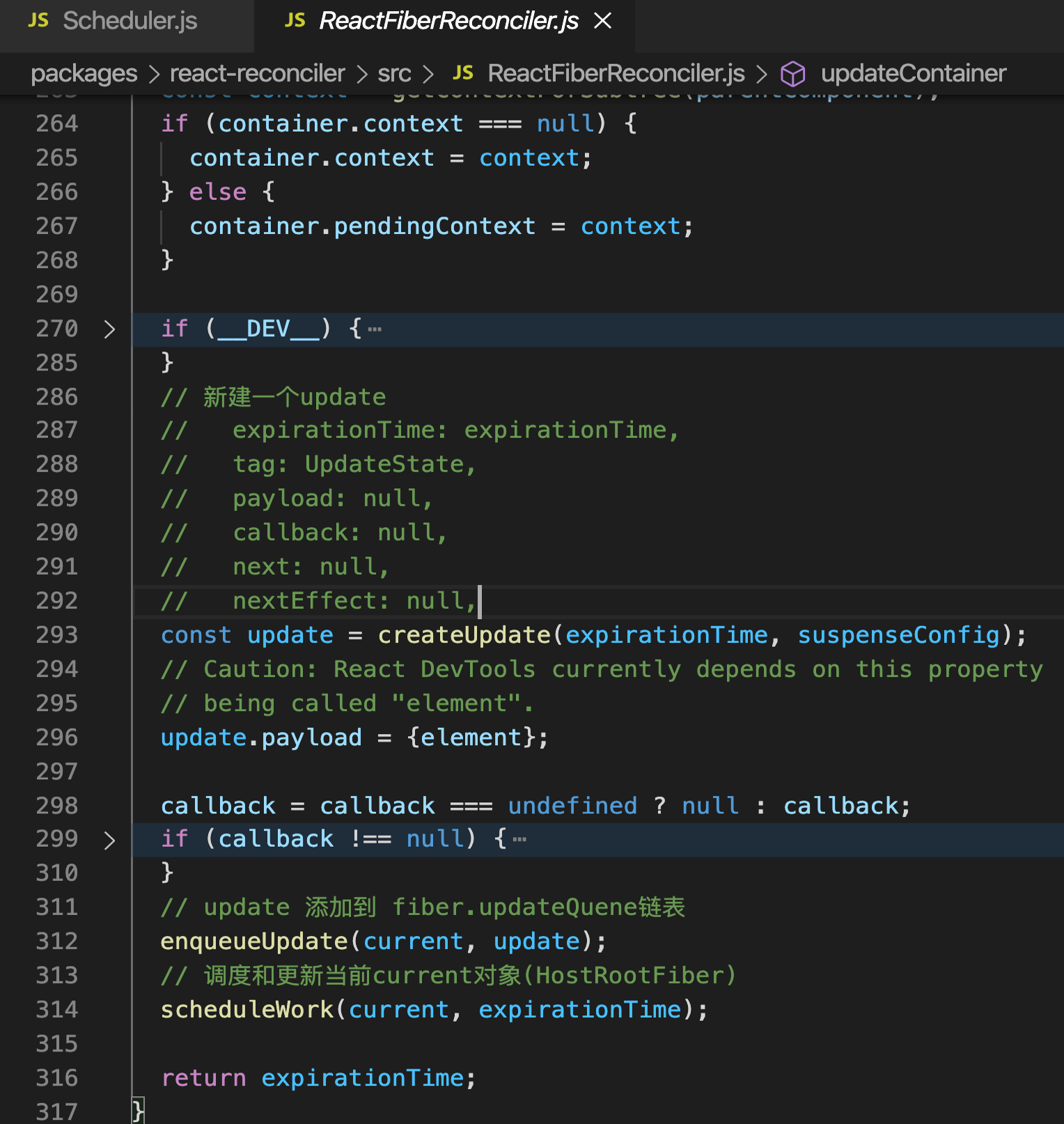
设置expirationTime, 过期时间,和优先级挂钩的
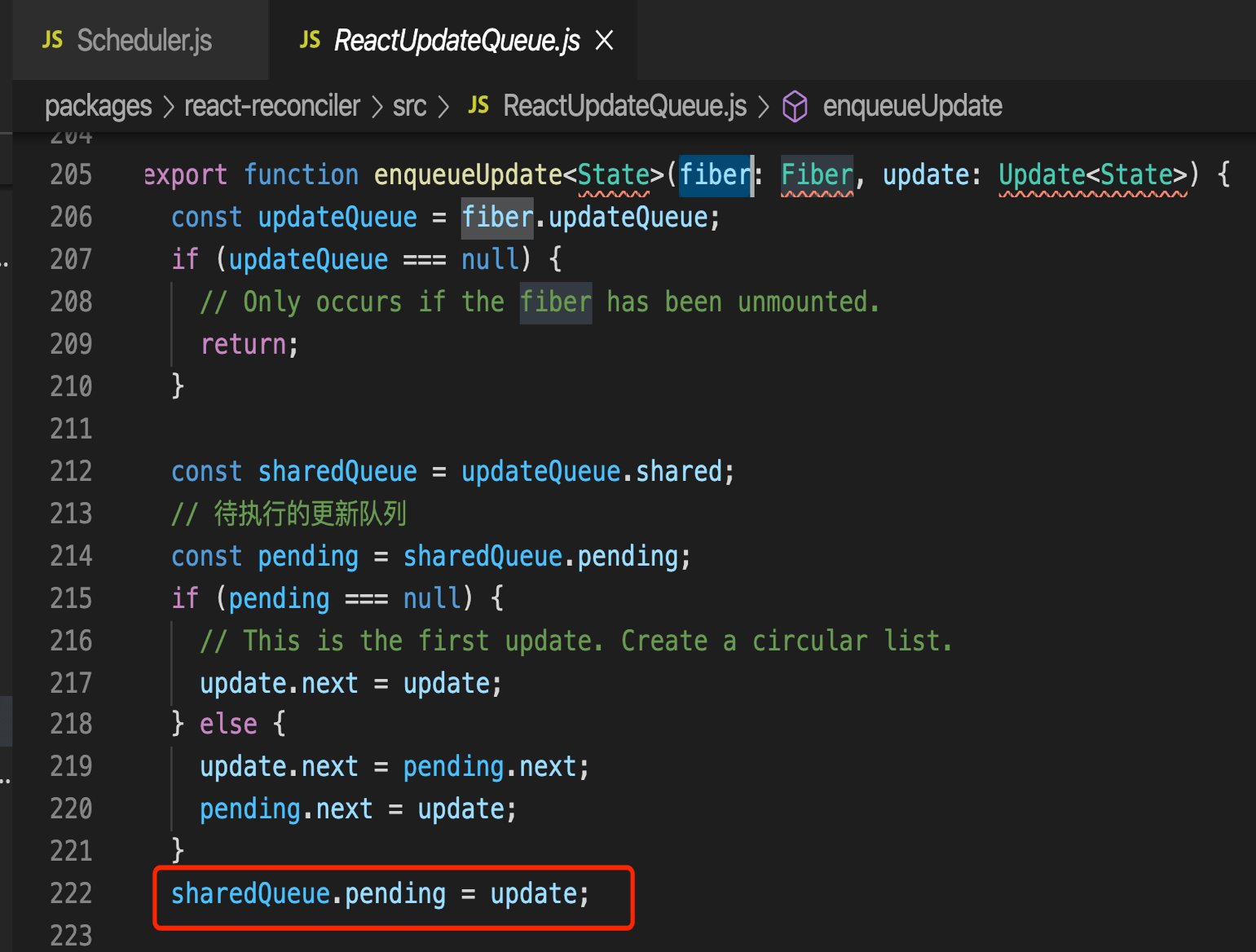
新建一个update,添加到fiber的updateQuene里
{ expirationTime: expirationTime, tag: UpdateState, payload: null, // element callback: null, // callback next: null, // 下一个update nextEffect: null, // 下一个副作用 }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8调用scheduleWork (调度流程)
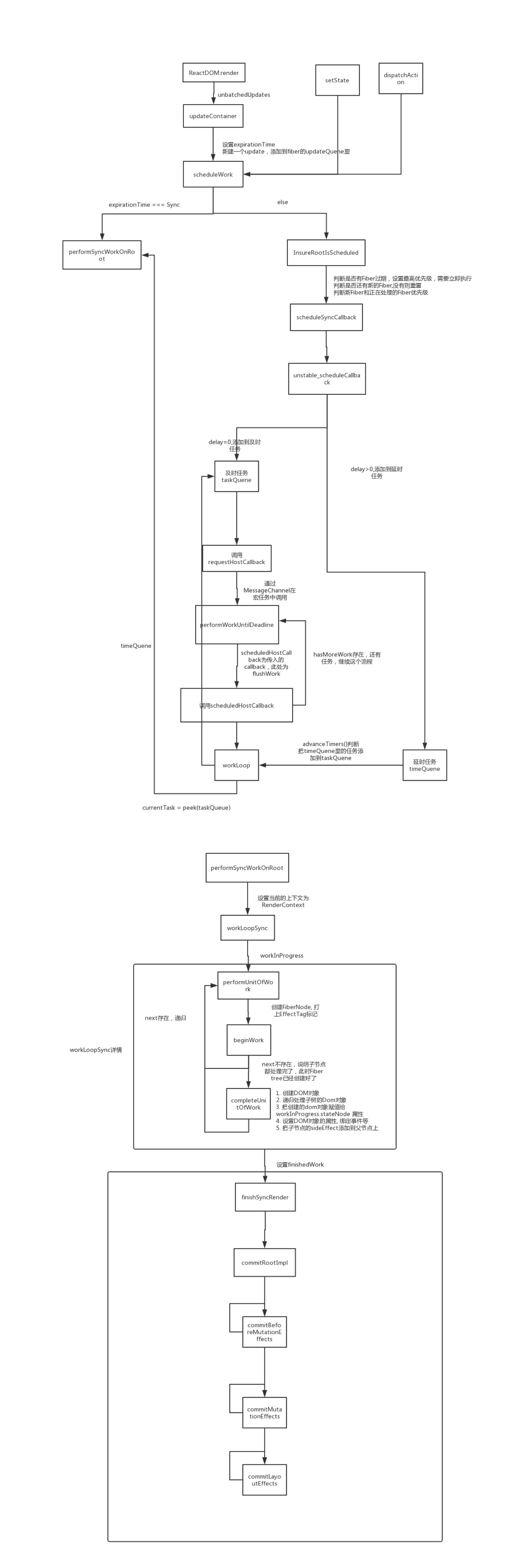
# scheduleWork
先找到FiberRoot
判断是否有高优先级任务打断当前正在执行的任务
如果是最高优先级而且处于unbatchUpdate下执行performSyncWorkOnRoot
其他调用 ensureRootIsScheduled 进入异步调度流程
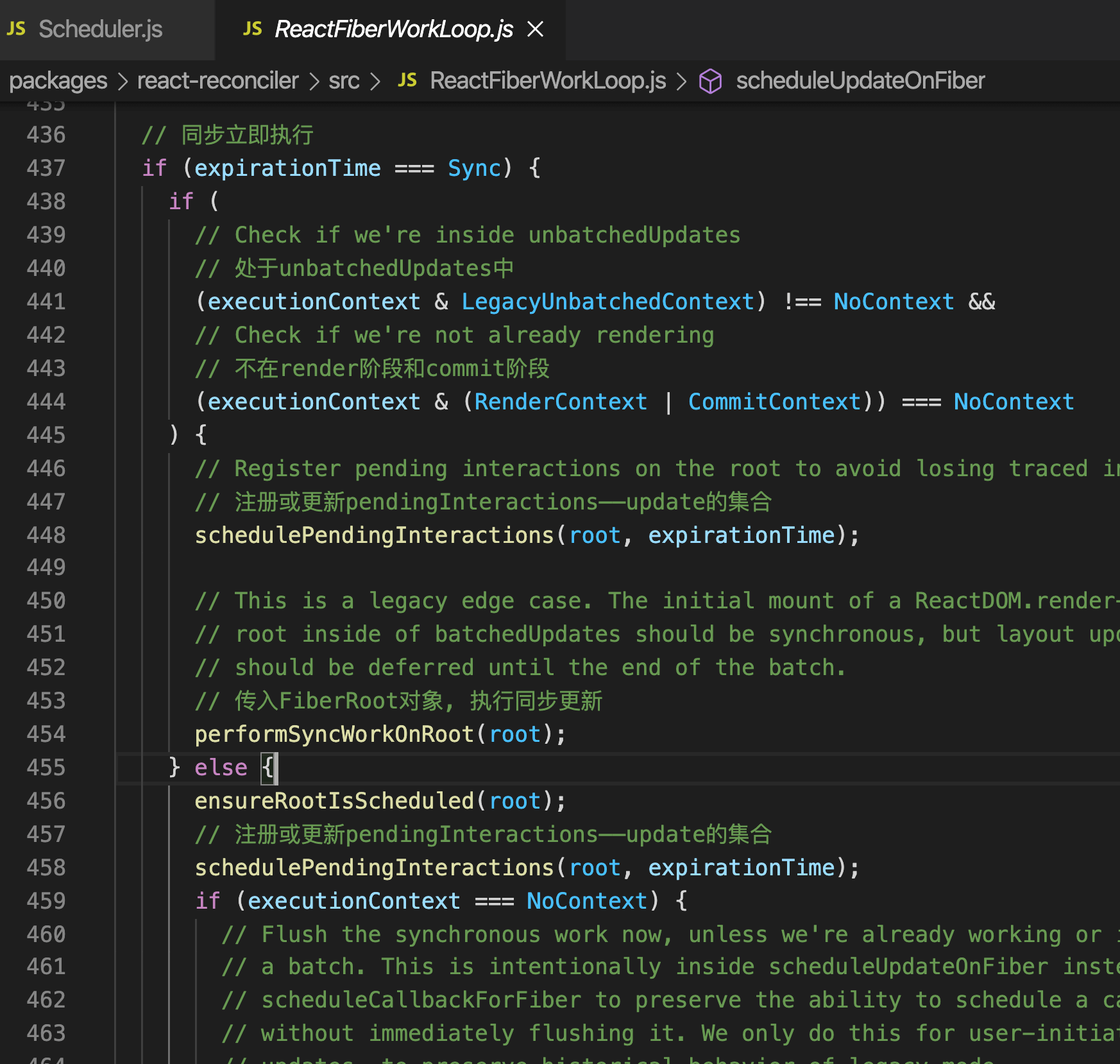
# ensureRootIsScheduled
此处会判断是否有优先级更高的任务进来,如果有,会中断现在的任务;如果没有,则继续执行
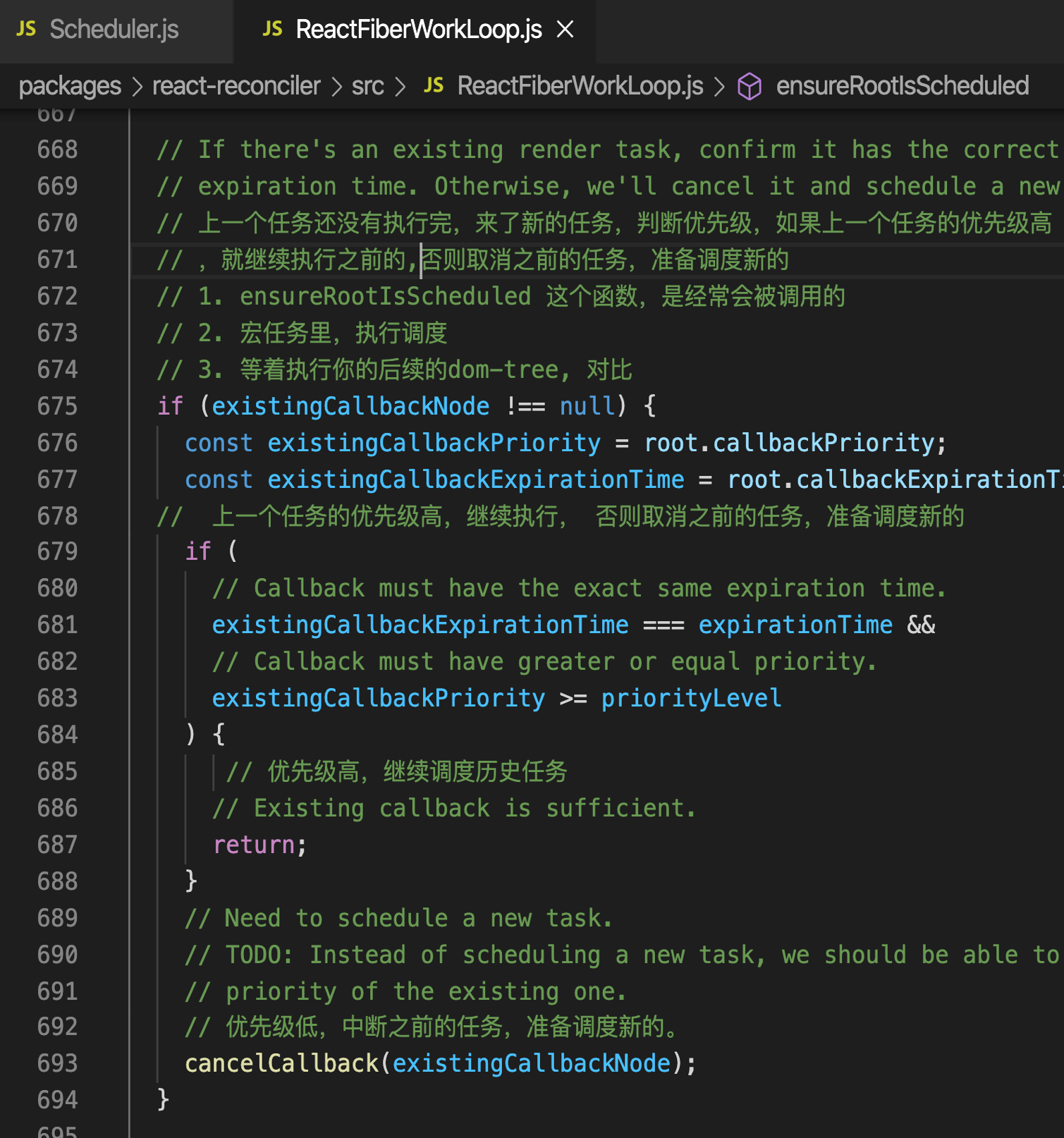
# unstable_scheduleCallback
- 区分延时任务(timeQuene)和及时任务(taskQuene),创建任务。
- 存在及时任务,则调用requestHostCallback
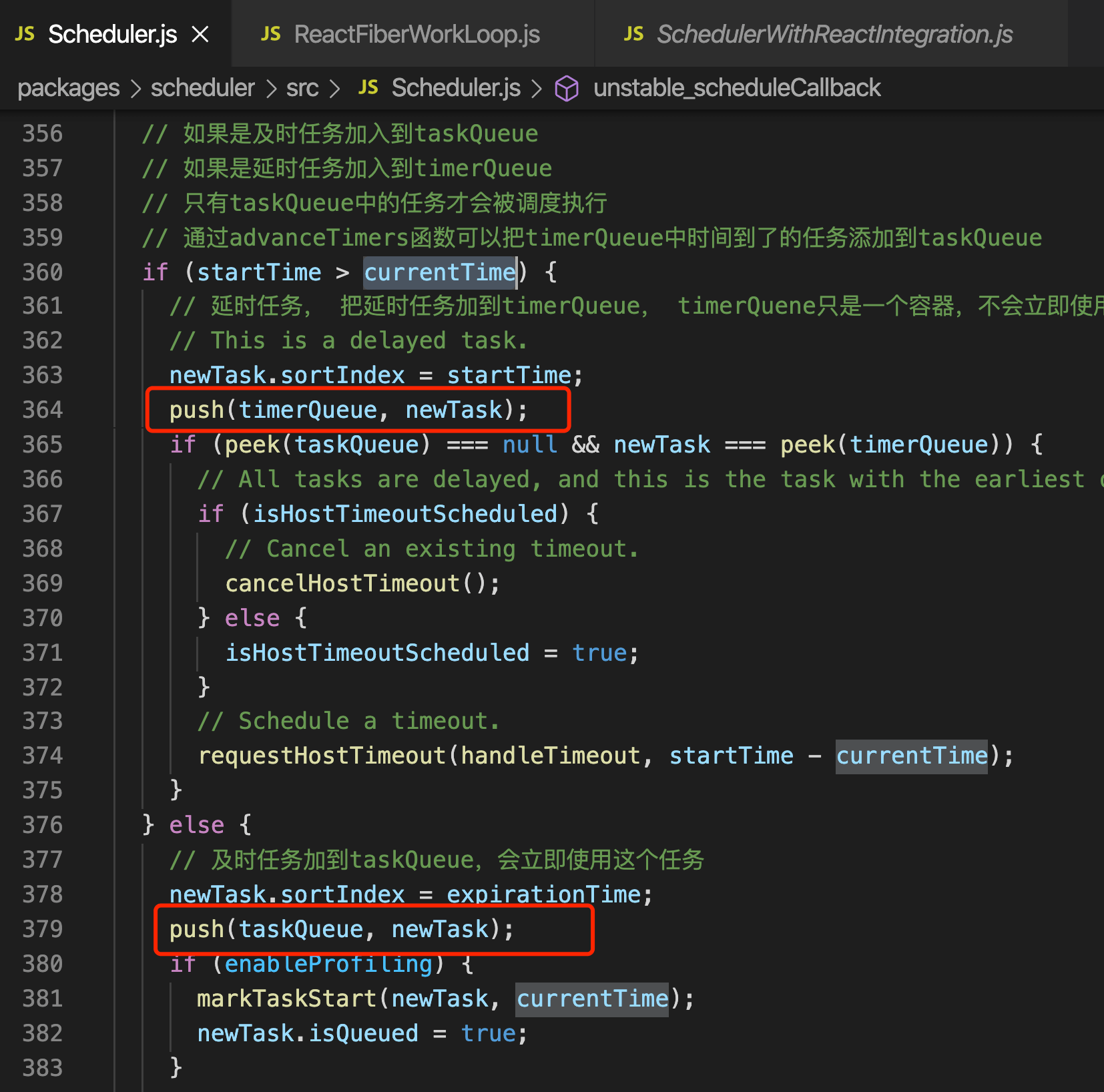
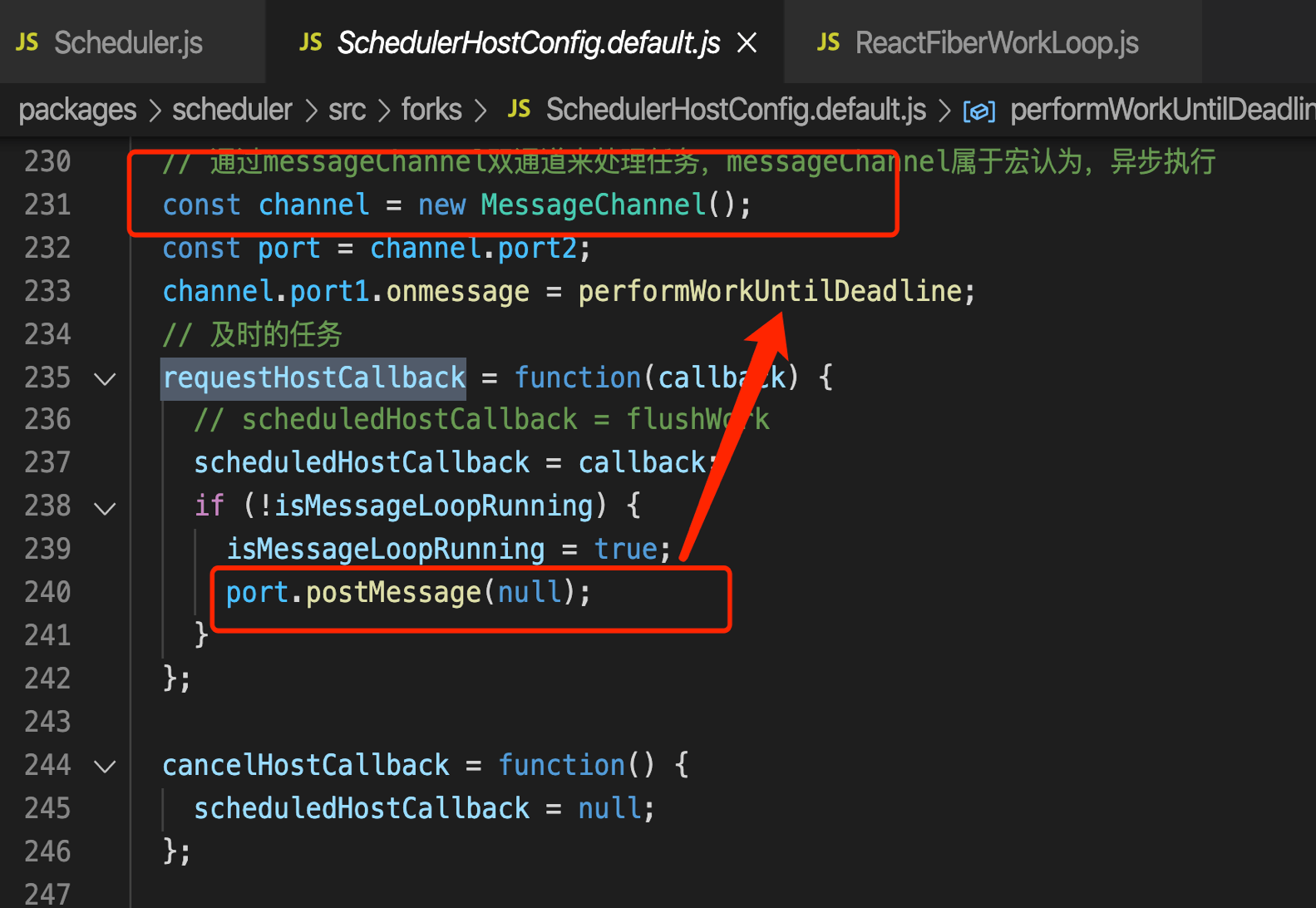
# requestHostCallback
创建MessageChannel
调用port.postMessage,根据MessageChannel的特性,调用port.postMassage之后,会在宏任务里执行performWorkUntilDeadLine
在performWorkUntilDeadLine会逐步根据当前时间把延时任务添加到及时任务
在宏任务中执行callback,也就是 performSyncWorkOnRoot
如果存在子任务,则递归执行performWorkUntilDeadLine

# performSyncWorkOnRoot
# workLoopSync
此处主要执行了3个操作:
- 标记上下文为RenderContext
- 执行workLoopSync 递归创建fiber tree标记副作用,render以及之前的生命周期都将在此阶段执行
- 调用finishSyncRender,渲染页面,执行剩下的生命周期
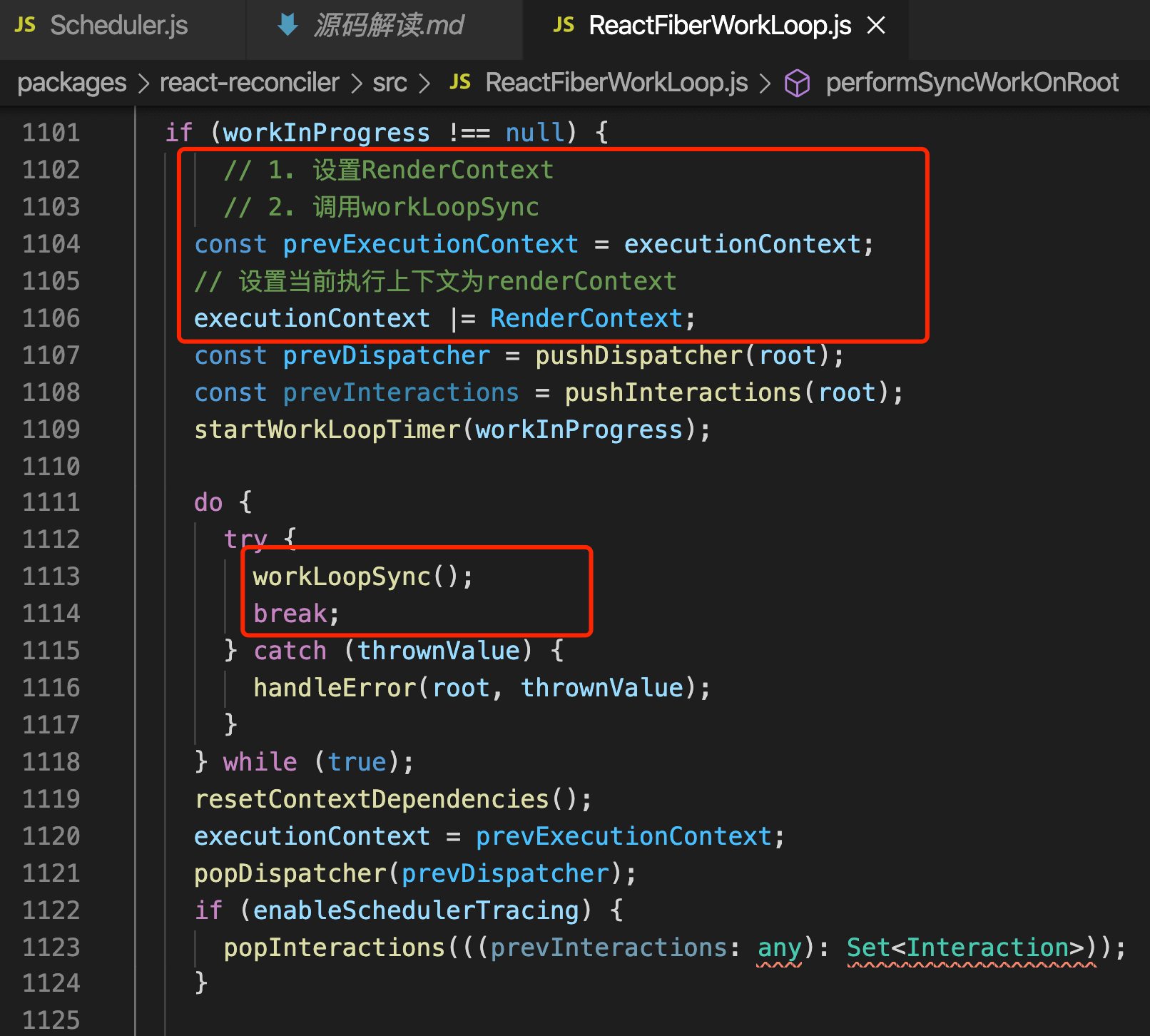

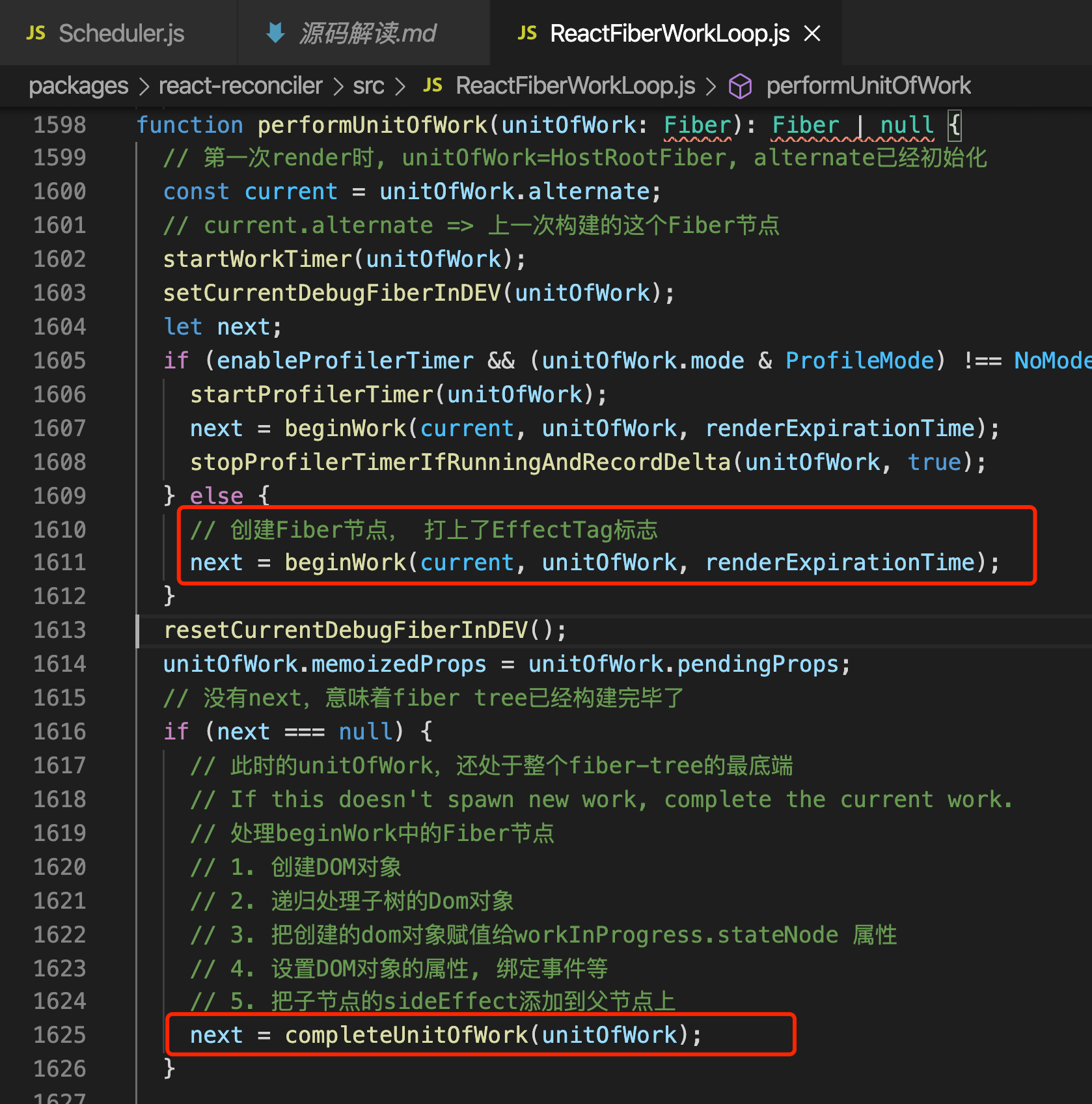
调用beginWork,在beginWork创建Fiber节点,如果Next节点不为空,继续处理next节点,直到next为null说明已经创建完整个Fiber tree了,之后调用completeUnitOfWork,创建Dom对象等。注意: completeUnitOfWork阶段虽然创建了dom对象,但是还不会渲染到页面上,只是保存着。
beginWork
- 初次则创建fiber节点
- 非初次则进行diff,打上Effect更新标记
- 执行render之前的生命周期,以及执行render 生命周期,获得子节点,继续循环执行beginWork
- 链接上父级节点,形成Fiber tree
completeUnitOfWork_处理beginWork中的Fiber节点
创建DOM对象
递归处理子树的Dom对象
把创建的dom对象赋值给workInProgress.stateNode 属性
设置DOM对象的属性, 绑定事件等
把子节点的sideEffect添加到父节点上
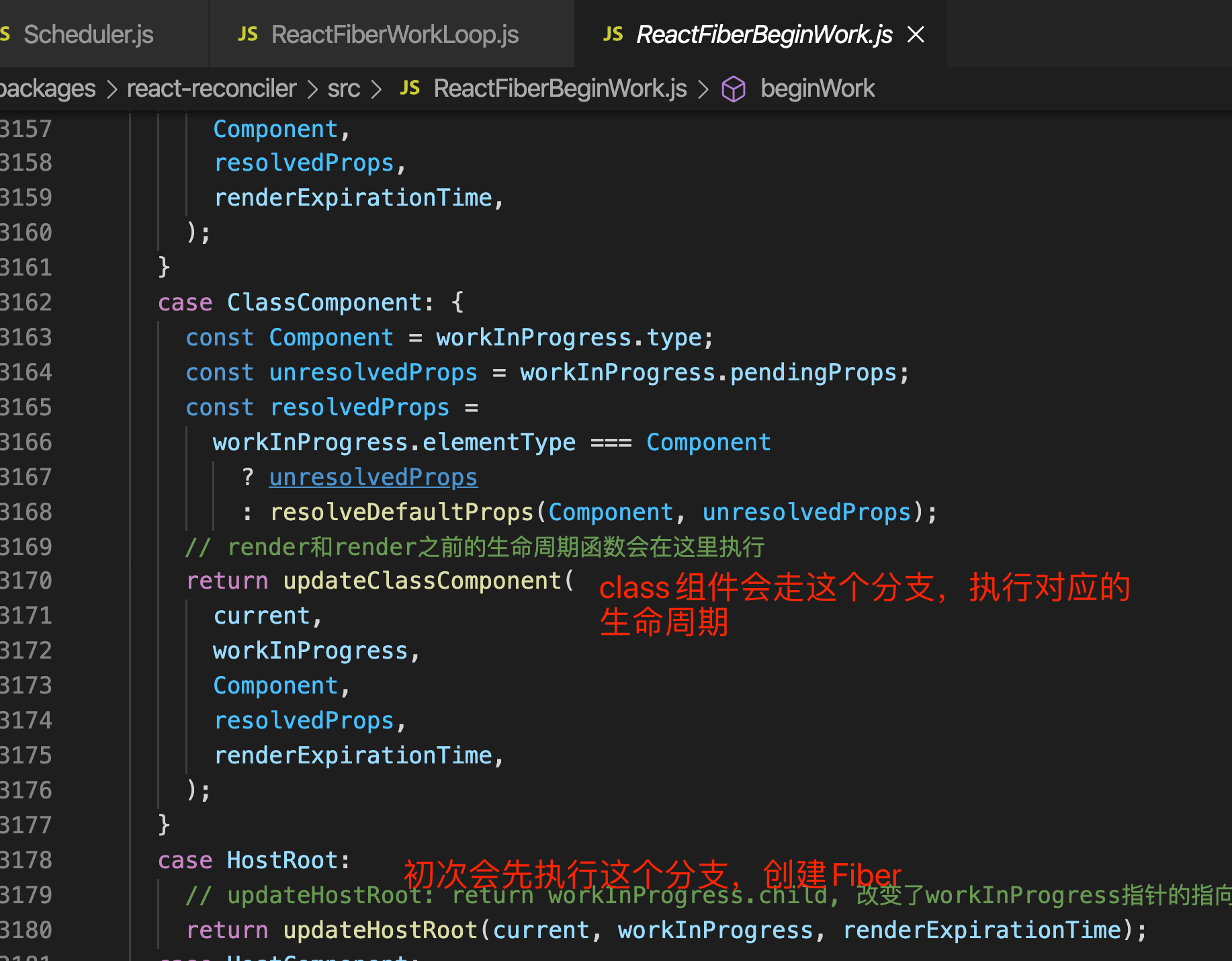
beginWork是一个各种react类型处理逻辑的一个聚合,我们挑选出其中的class component情况来看一下
这里分为初始化和更新两种情况,最终的结构都是得到子Fiber节点,并且fiber节点被打上了EffectTag标记
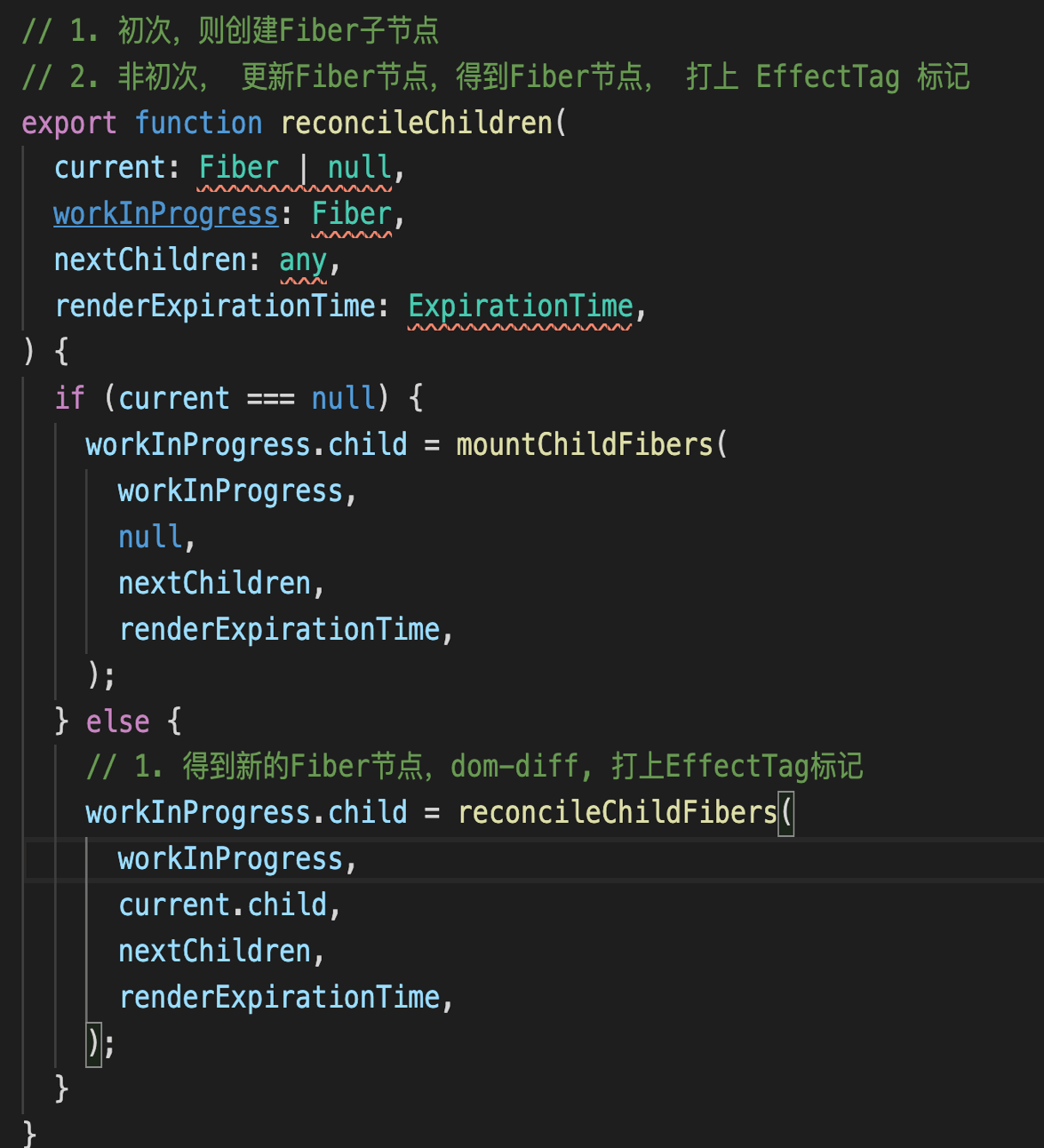
初次创建Fiber,不需要diff
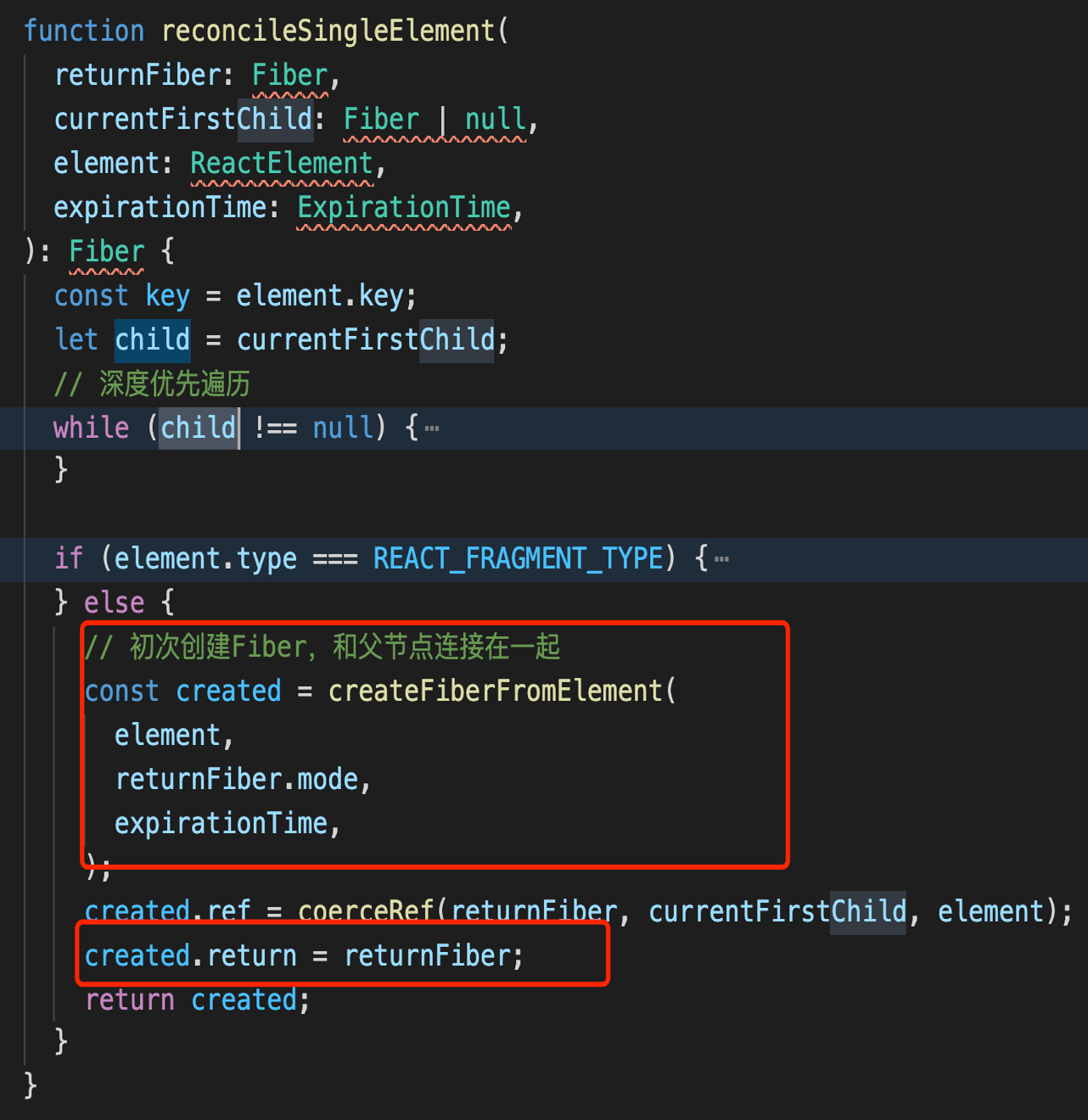
非初次,diff的情况
执行生命周期:
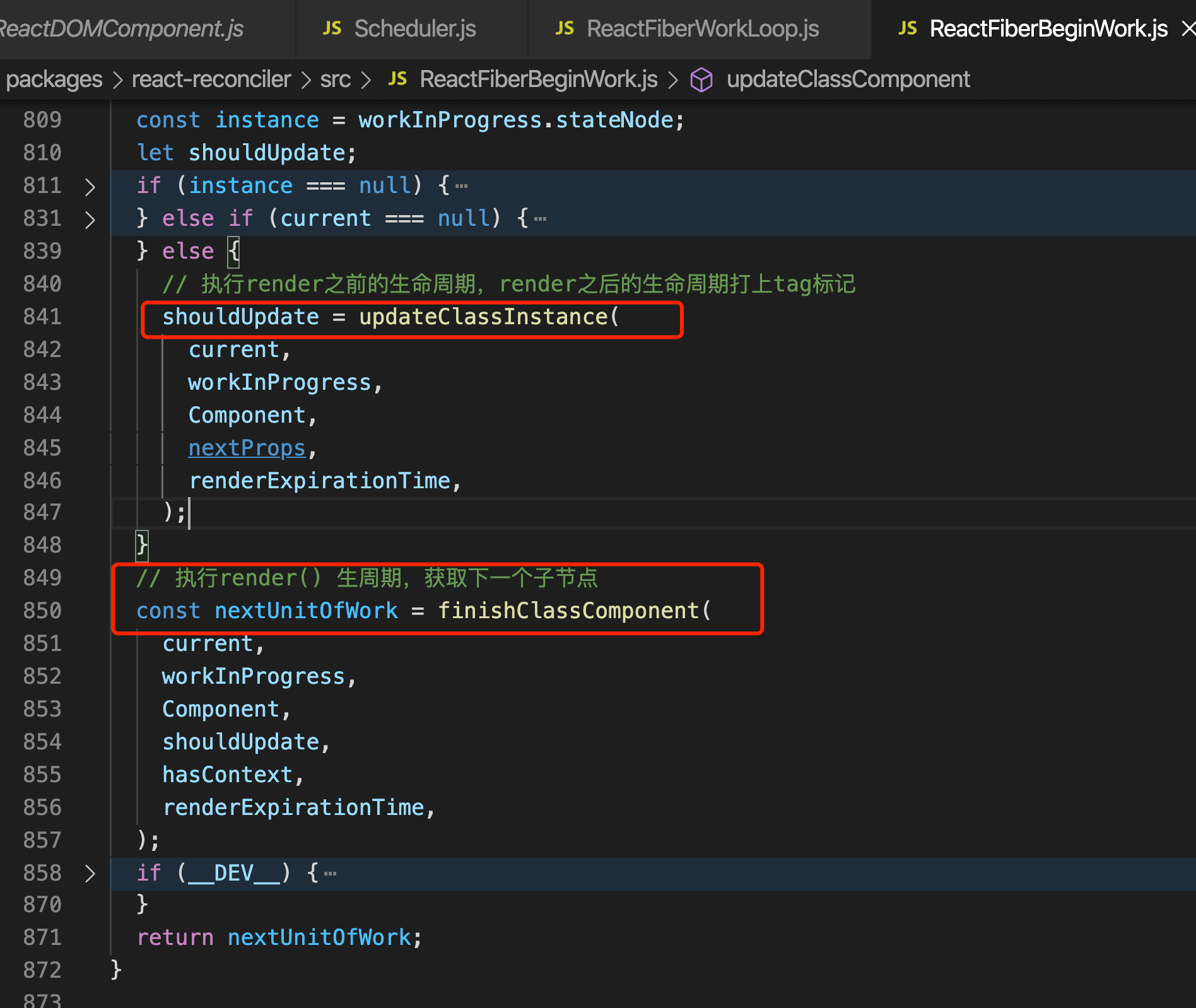
- 先执行render之前的生命周期
- 执行render生命周期得到子节点, 继续遍历子节点
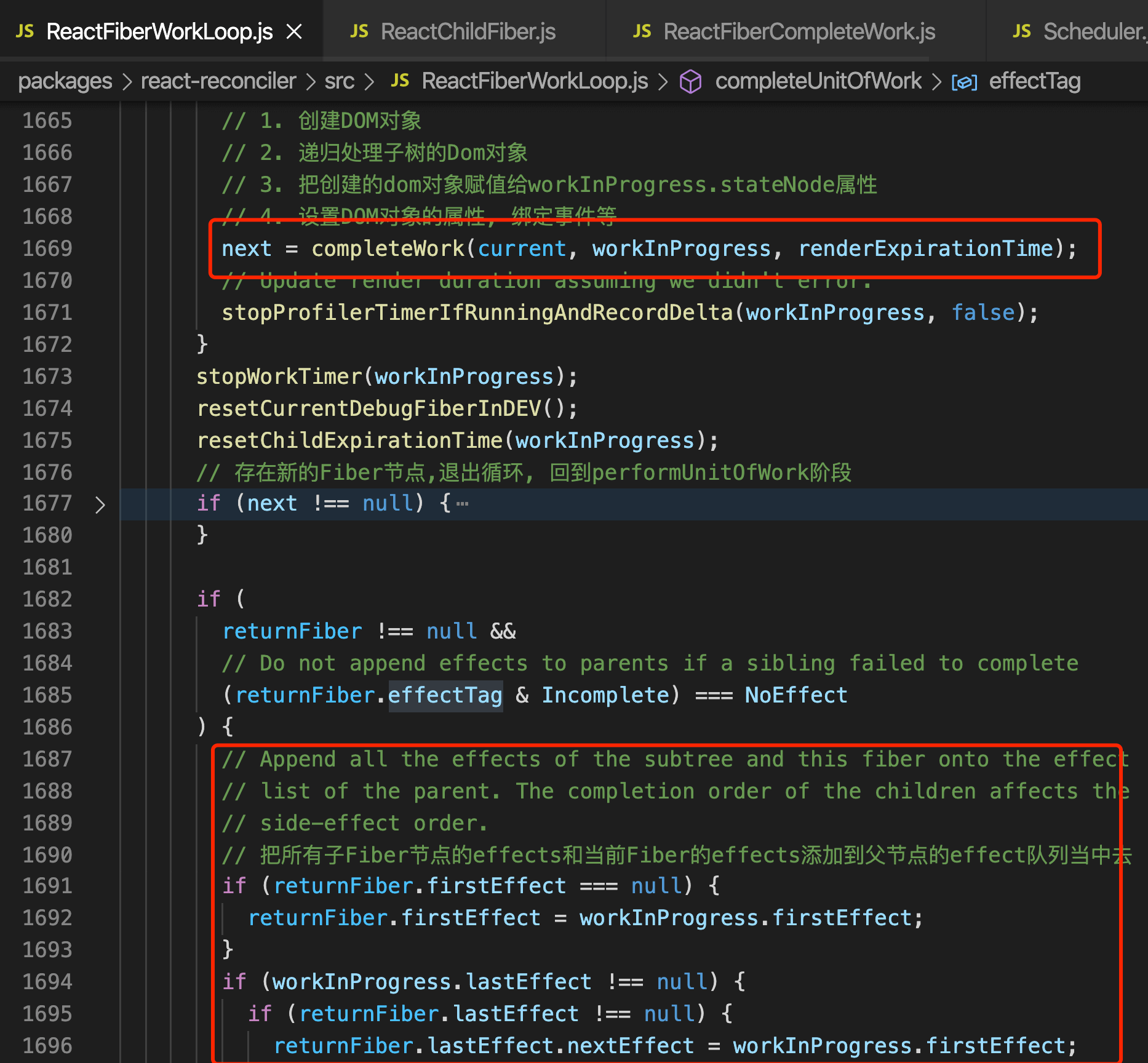
beginWork执行完了,现在fiber tree也创建完毕了,每个节点的side Effect也设置了接下来就是该处理所有的副作用,创建Dom了这里会做以下几件事:
- 调用completeWork,创建Dom
- 把所有子Fiber节点的effects和当前Fiber的effects添加到父节点的effect队列当中去
- 回到父节点,继续向上遍历
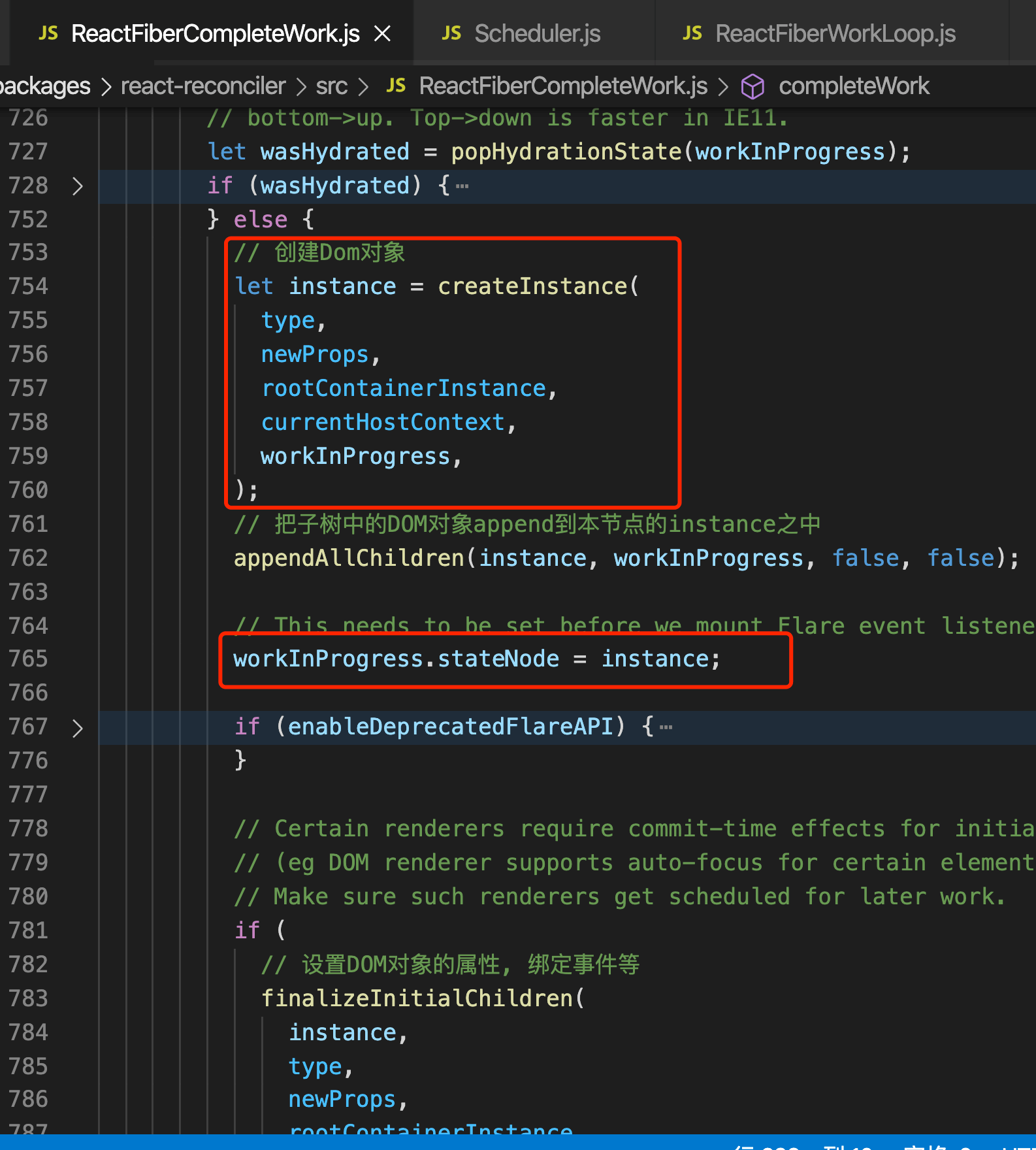
completeWork做了以下几件事:
创建DOM对象
递归处理子树的Dom对象
把创建的dom对象赋值给workInProgress.stateNode属性
设置DOM对象的属性, 绑定事件等
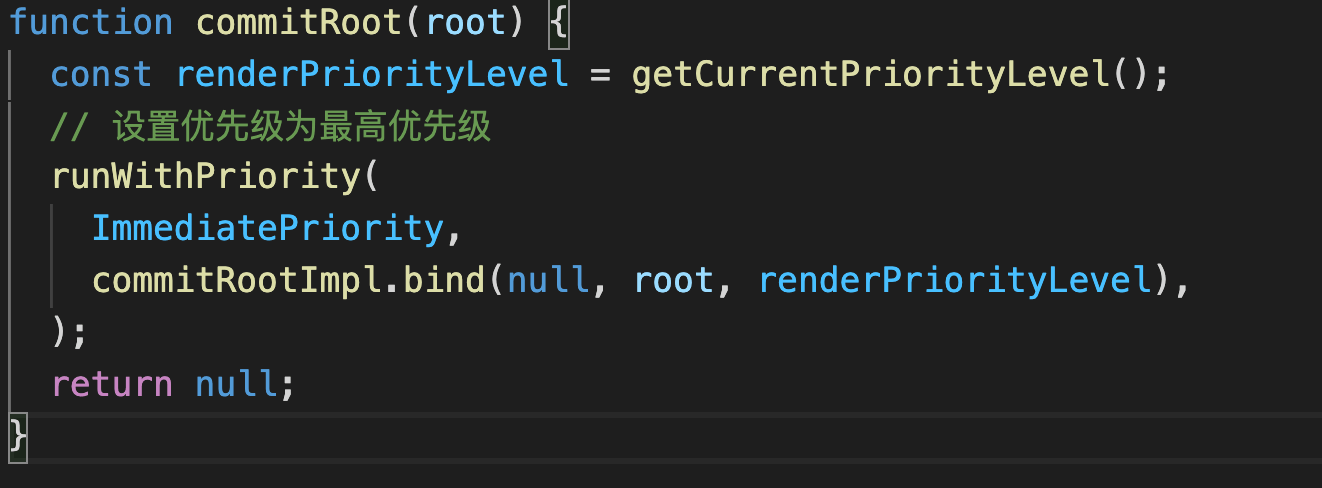
# finishSyncRender
finishSyncRender是整个流程的最后一步了,它做了以下:
设置优先级为最高优先级
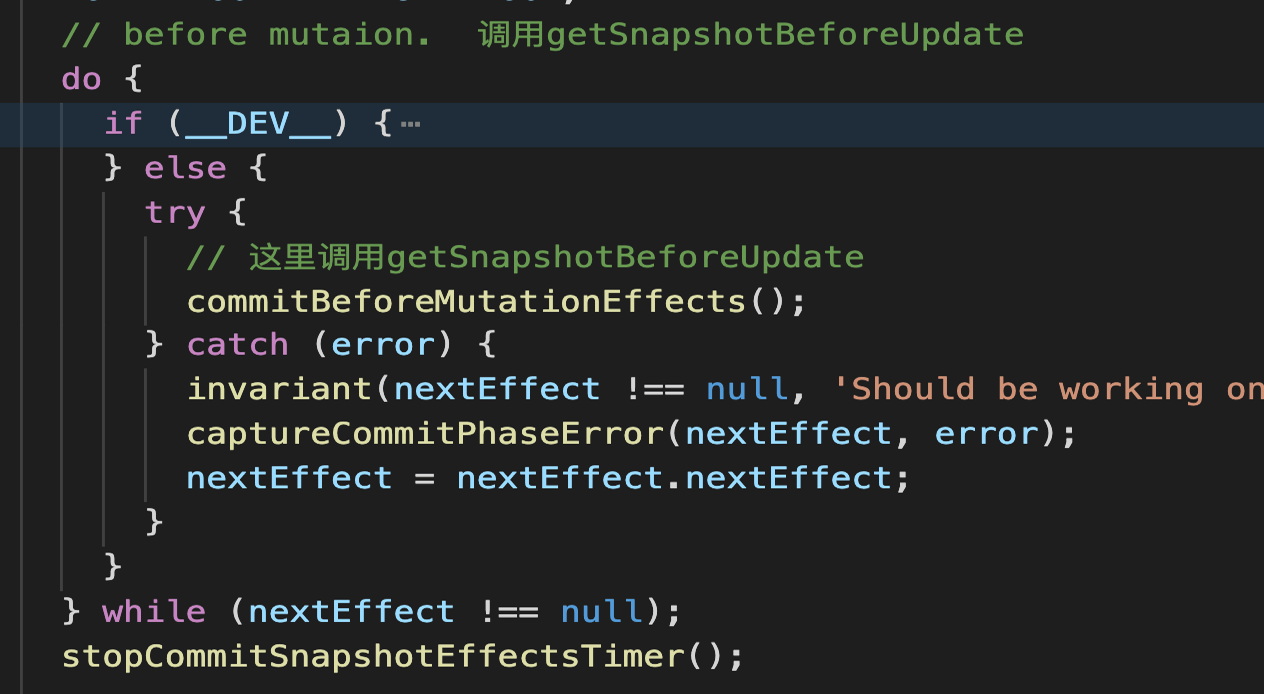
递归调用commitBeforeMutationEffects,此方法会调用 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate生命周期
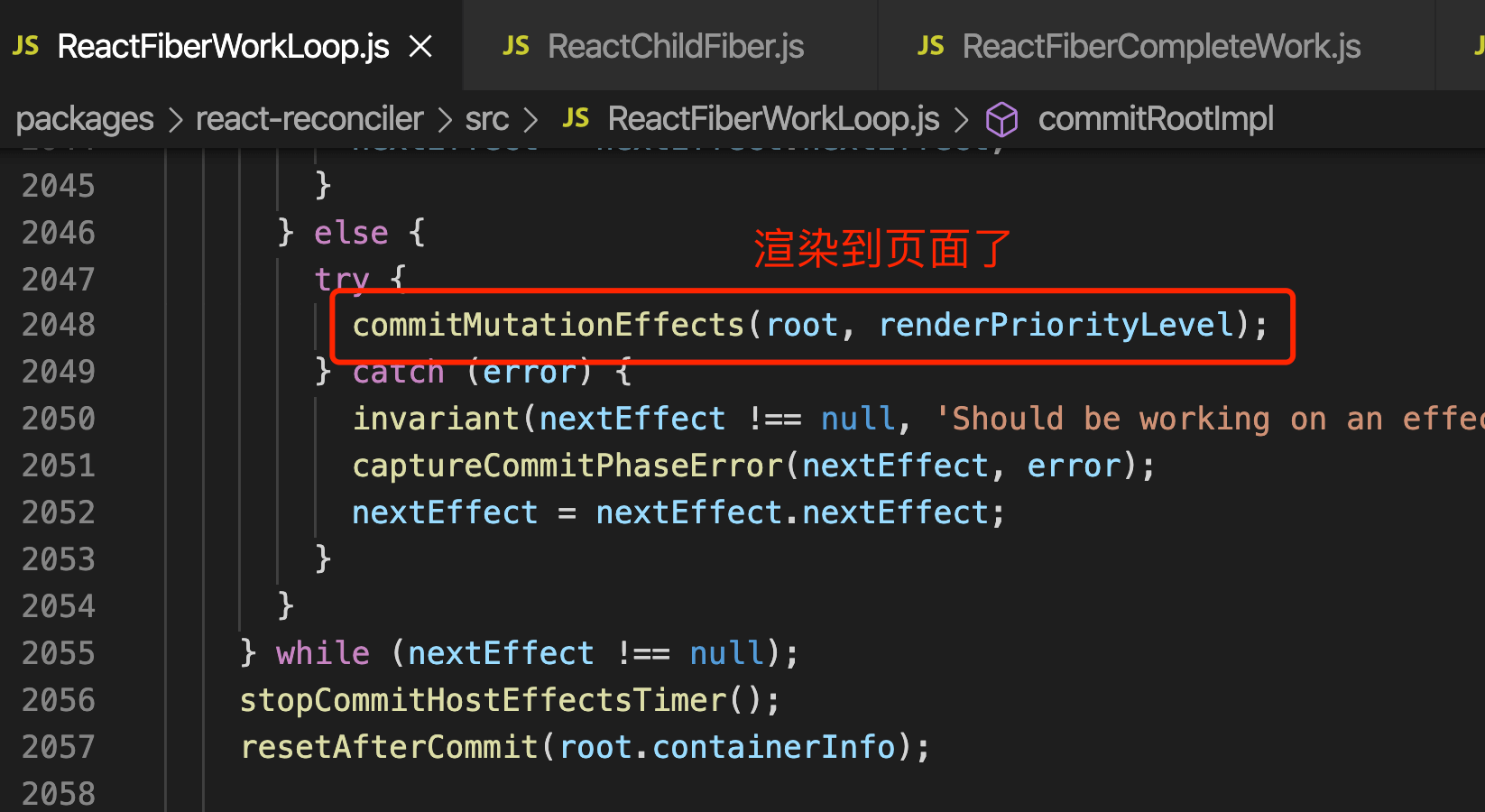
递归调用commitMutationEffects,渲染到页面上
递归调用commitLayoutEffects,执行didMount/didUpdate生命周期
第一个while
第二个while
第三个while
# ensureRootIsScheduled
判断是否有任务过期,设置最高优先级,需要立即执行
没有新的任务,重置
上一个任务还没有执行完,来了新的任务,判断优先级,如果上一个任务的优先级高,就继续执行之前的 否则取消之前的任务,准备调度新的
执行scheduleSyncCallback/scheduleCallback => unstable_scheduleCallback
- 分成了及时任务,和延时任务
- 在执行performSyncWorkOnRoot之前,会判断把延时任务加到及时任务里面来
- 如果任务超过了 timeout ,任务会过期
- 通过messageChanel,这个宏任务,来在下一次的事件循环里调用performSyncWorkOnRoot
# 更新state是怎么执行的
this.setState()到底是同步还是异步的? 这个setState是在哪里调用的?
生命周期里里调用 isRendering=true 不再走接下来的流程
事件系统回调里面 isBatchingUpdates=true 批处理的状态
unbatchUpdate 立即就执行了, setTimeout里
batchUpdate isBatchingUpdates=true 批处理的状态